ABOUT Palenque
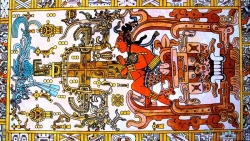
Palenque, also anciently known as Lakamha (literally: "Big Water"), was a Maya city state in southern Mexico that flourished in the 7th century. The Palenque ruins date from ca. 226 BC to ca. 799 AD. After its decline, it was overgrown by the jungle of cedar, mahogany, and sapodilla trees, but has since been excavated and restored. It is located near the Usumacinta River in the Mexican state of Chiapas, about 130 km (81 mi) south of Ciudad del Carmen, 150 meters (490 ft) above sea level. It averages a humid 26 °C (79 °F) with roughly 2,160 millimeters (85 in) of rain a year.Palenque is a medium-sized site, smaller than Tikal, Chichen Itza, or Copán, but it contains some of the finest architecture, sculpture, roof comb and bas-relief carvings that the Mayas produced. Much of the history of Palenque has been reconstructed from reading the hieroglyphic inscriptions on the many monuments; historians now have a long sequence of the ruling dynasty of Palenque in the 5th century and extensive knowledge of the city-state's rivalry with other states such as Calakmul and Toniná. The most famous ruler of Palenque was K'inich Janaab Pakal, or Pacal the Great, whose tomb has been found and excavated in the Temple of the Inscriptions.
By 2005, the discovered area covered up to 2.5 km2 (1 sq mi), but it is estimated that less than 10% of the total area of the city is explored, leaving more than a thousand structures still covered by jungle. Palenque received 920,470 visitors in 2017.
Mythological beings using a variety of emblem glyphs in their titles suggests a complex early history. For instance, Kʼukʼ Bahlam I, the supposed founder of the Palenque dynasty, is called a Toktan Ajaw in the text of the Temple of the Foliated Cross.
The famous structures that we know today probably represent a rebuilding effort in response to the attacks by the city of Calakmul and its client states in 599 and 611. One of the main figures responsible for rebuilding Palenque and for a renaissance in the city's art and architecture is also one of the best-known Maya Ajaw, Kʼinich Janaabʼ Pakal (Pacal the Great), who ruled from 615 to 683. He is known through his funerary monument dubbed the Temple of Inscriptions, after the lengthy text preserved in the temple's superstructure. At the time Alberto Ruz Lhuillier excavated Pakal's tomb, it was the richest and best preserved of any scientifically excavated burial then known from the ancient Americas. It held this position until the discovery of the rich Moche burials at Sipan, Peru and the recent discoveries at Copan and Calakmul.
A bas-relief in the Palenque museum that depicts Upakal K'inich, the son of K'inich Ahkal Mo' Naab III.
Beside the attention that K'inich Janaab' Pakal's tomb brought to Palenque, the city is historically significant for its extensive hieroglyphic corpus composed during the reigns of Janaab' Pakal, his son Kʼinich Kan Bahlam II, and his grandson K'inich Akal Mo' Naab', and for being the location where Heinrich Berlin and later Linda Schele and Peter Mathews outlined the first dynastic list for any Maya city. The work of Tatiana Proskouriakoff as well as that of Berlin, Schele, Mathews, and others, initiated the intense historical investigations that characterized much of the scholarship on the ancient Maya from the 1960s to the present. The extensive iconography and textual corpus has also allowed for study of Classic period Maya mythology and ritual practice.[
By 2005, the discovered area covered up to 2.5 km2 (1 sq mi), but it is estimated that less than 10% of the total area of the city is explored, leaving more than a thousand structures still covered by jungle. Palenque received 920,470 visitors in 2017.
Mythological beings using a variety of emblem glyphs in their titles suggests a complex early history. For instance, Kʼukʼ Bahlam I, the supposed founder of the Palenque dynasty, is called a Toktan Ajaw in the text of the Temple of the Foliated Cross.
The famous structures that we know today probably represent a rebuilding effort in response to the attacks by the city of Calakmul and its client states in 599 and 611. One of the main figures responsible for rebuilding Palenque and for a renaissance in the city's art and architecture is also one of the best-known Maya Ajaw, Kʼinich Janaabʼ Pakal (Pacal the Great), who ruled from 615 to 683. He is known through his funerary monument dubbed the Temple of Inscriptions, after the lengthy text preserved in the temple's superstructure. At the time Alberto Ruz Lhuillier excavated Pakal's tomb, it was the richest and best preserved of any scientifically excavated burial then known from the ancient Americas. It held this position until the discovery of the rich Moche burials at Sipan, Peru and the recent discoveries at Copan and Calakmul.
A bas-relief in the Palenque museum that depicts Upakal K'inich, the son of K'inich Ahkal Mo' Naab III.
Beside the attention that K'inich Janaab' Pakal's tomb brought to Palenque, the city is historically significant for its extensive hieroglyphic corpus composed during the reigns of Janaab' Pakal, his son Kʼinich Kan Bahlam II, and his grandson K'inich Akal Mo' Naab', and for being the location where Heinrich Berlin and later Linda Schele and Peter Mathews outlined the first dynastic list for any Maya city. The work of Tatiana Proskouriakoff as well as that of Berlin, Schele, Mathews, and others, initiated the intense historical investigations that characterized much of the scholarship on the ancient Maya from the 1960s to the present. The extensive iconography and textual corpus has also allowed for study of Classic period Maya mythology and ritual practice.[